news
<
A vacuum pump is a device that uses various methods to generate, improve and maintain vacuum in a closed space. A vacuum pump can be defined as a device or device that uses mechanical, physical, chemical or physicochemical methods to evacuate the evacuated container to obtain a vacuum.
With the development of vacuum applications, there are many kinds of vacuum pumps, whose pumping speed ranges from a few tenths of a liter per second to hundreds of thousands or millions of liters per second. The ultimate pressure (ultimate vacuum) ranges from rough vacuum to extremely high vacuum above 10-12Pa.

Classification of vacuum pumps
According to the working principle of vacuum pumps, vacuum pumps can basically be divided into two types, namely variable displacement vacuum pumps and momentum transfer pumps. The variable displacement vacuum pump is a vacuum pump that uses the periodic change of the volume of the pump chamber to complete suction and exhaust to achieve the purpose of pumping. Gas is compressed before exiting the pump chamber. Momentum transfer pumps (molecular vacuum pumps) rely on high-speed rotating blades or high-speed jets to transfer momentum to gas or gas molecules, so that the gas is continuously transferred from the pump inlet to the outlet. (Introduction in a separate section) Variable displacement vacuum pumps are divided into: reciprocating type, rotary type (rotary vane type, slide valve type, liquid ring type, Roots type, screw type, claw rotor type), and other types.

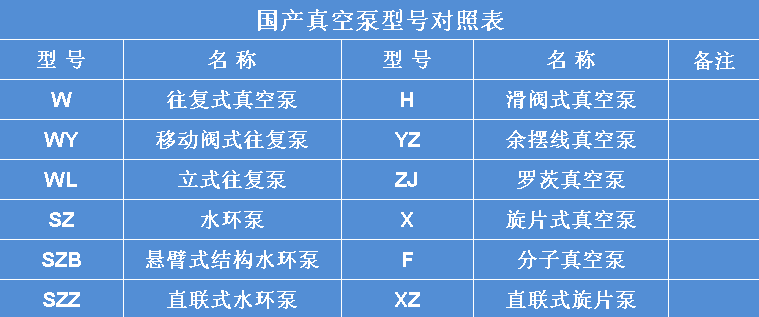
Vacuum pump specifications and model representation
The models of various domestic mechanical vacuum pumps are usually expressed in Chinese pinyin letters. The Chinese Pinyin letter indicates the type of pump; the number before the letter indicates the number of stages of the pump, and "1" is omitted for single stage; the number after the horizontal line after the letter indicates the pumping speed (L/S)
steam jet pump
Wet pumps (liquid ring vacuum pumps, rotary vane pumps)
Dry pumps (Roots pumps, screw pumps, claw pumps)
1. Steam jet pump
The working principle of the jet vacuum pump: the steam jet vacuum pump is a vacuum pump equipment with a certain pressure. The steam passes through the Laval nozzle, decompresses and accelerates, the potential energy of the steam is converted into kinetic energy and sprayed into the mixing chamber at supersonic speed, and mixed with the pumped medium. For energy exchange, the mixed gas enters the diffuser, decelerates and pressurizes, and the motion is converted into pressure energy. In order to reduce the pumping load of the back-stage pump, a condenser is configured to convect through two media with a certain temperature difference to perform heat transfer. Exchange, to achieve the purpose of condensing high-temperature medium, and discharge to atmospheric pressure.
2. Wet pump: liquid ring vacuum pump
Inside the circular pump body (A), an impeller (B) is mounted on an eccentric shaft relative to the center line of the pump body. The centrifugal action of the rotating impeller forces the working fluid to flow through the channel (D) to the periphery of the cavity to form a circular flow (C).
When the pump works, the conveyed gas mixture enters the impeller through the suction port (H) on the middle plate (E), forming a vacuum at the pump inlet. The gas mixture is filled into the impeller chamber located between the inner diameter of the liquid ring and the root of the impeller blades. As the impeller rotates, the degree to which the impeller blades are submerged in the liquid ring increases, reducing the volume between the liquid ring and the root of the impeller blades. The result is that the gas mixture is compressed until it reaches the discharge (J) in the middle plate (K). The gas mixture exits through the discharge port.
During the compression cycle, heat is transferred to the liquid ring. In order to keep the temperature below the evaporation point of the working fluid, cooling is necessary. Cooling is achieved by continuously adding cold working fluid to the liquid ring. The amount of working fluid added is equal to the amount of working fluid discharged through the discharge port together with the compressed gas mixture. The gas mixture and working fluid are finally separated through the pump outlet.
3. Dry pump
Dry vacuuming: no pollution from industrial production flow;
Deep vacuum, more flexible operation;
No waste water, no pollution, (less or) no waste disposal costs;
Lower maintenance costs;
Recover solvent immediately at the pump discharge;
Low consumption of water, electricity, gas, etc. → low operating costs.
Dry pump cost
The investment cost is higher, but the running cost is lower.
Extend service intervals and bearing life.
Within the operating range, power consumption is low. Therefore, the energy saving effect is better in terms of capacity ratio (M3/hr/kW).
No contaminated oil to be disposed of (except for gearboxes).
Dry pump technology: pump types: roots pumps, screw pumps, claw pumps;
Ring pumps can be divided into the following types according to different structures:
(1) Single-stage single-acting liquid ring pump single-stage means that there is only one impeller, and single-acting means that each time the impeller rotates, suction and exhaust are performed once. This type of pump has a higher ultimate vacuum, but lower pumping speed and efficiency.
(2) Single-stage double-acting liquid ring pump single-stage means that there is only one impeller, and double-acting means that each time the impeller rotates, the suction and exhaust are performed twice. Under the same pumping speed condition, the double acting liquid ring pump greatly reduces the size and weight compared with the single acting liquid ring pump. Since the working chamber is symmetrically distributed on both sides of the pump hub, the load acting on the rotor is improved. This type of pump has a higher pumping speed and higher efficiency.
(3) Most of the two-stage liquid ring pumps are single-acting pumps connected in series. In essence, the impellers of two single-stage single-acting liquid ring pumps are connected by a common shaft. Its main feature is that it still has a large pumping speed under a relatively high vacuum degree, and its working condition is stable.
(4) Atmospheric liquid ring pump is actually a unit of atmospheric ejector series liquid ring pump. The atmospheric pump connected in series in front of the liquid ring pump is to increase the ultimate vacuum and expand the application range of the pump.
PRODUCTS
















