CVD
CVD (chemical vapor deposition)
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a method that chemical gas or vapor react on the surface of substrate to synthesize coatings or nano materials. It is the most widely used technology in semiconductor industry to deposit a variety of materials, including a wide range of insulating materials, most metal materials and metal alloys. Theoretically, it is very simple: two or more gaseous raw materials are introduced into a reaction chamber, and then they react with each other to form a new material, which is deposited on the wafer surface. A good example is the deposition of silicon nitride film (Si3N4), which is formed by the reaction of silane and nitrogen.
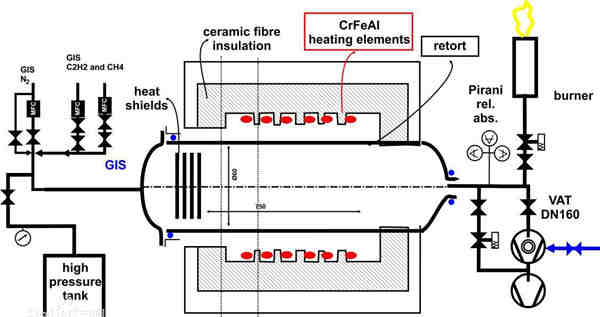
Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) is a traditional technique for preparing thin films. The principle of CVD is to use gaseous precursor reactants to decompose some components of gaseous precursor through chemical reactions between atoms and molecules to form thin films on the substrate. Chemical vapor deposition includes atmospheric pressure chemical vapor deposition, plasma assisted chemical deposition, laser assisted chemical deposition, metal organic compound deposition and so on.
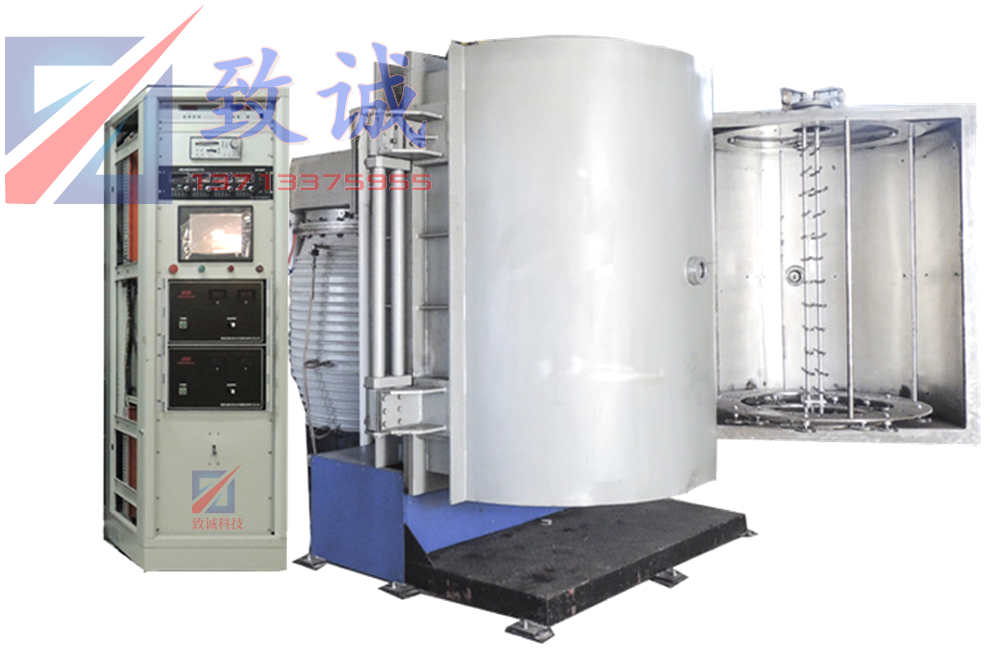
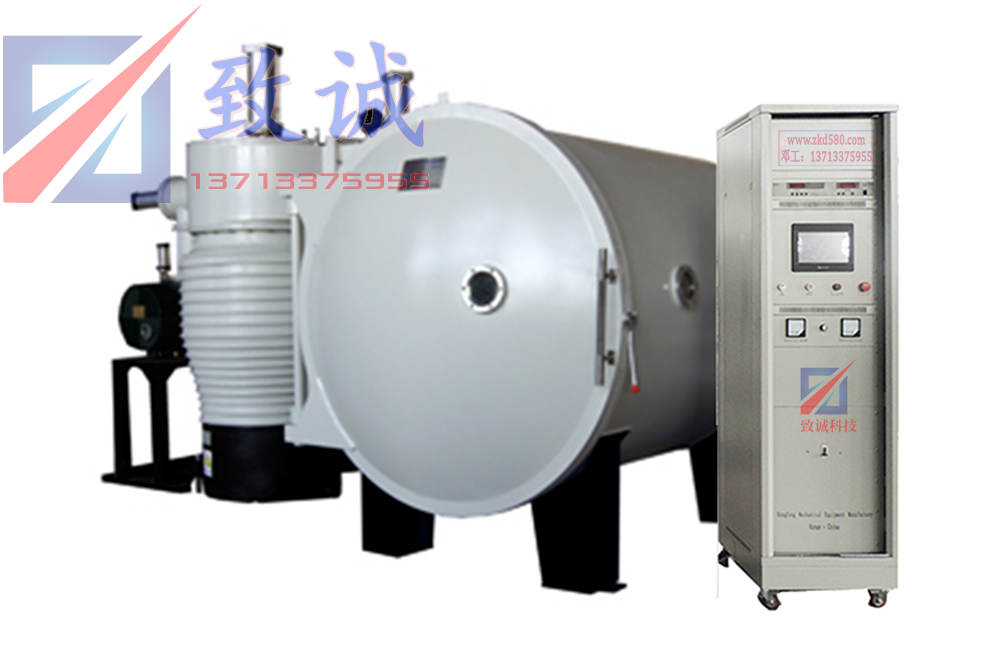
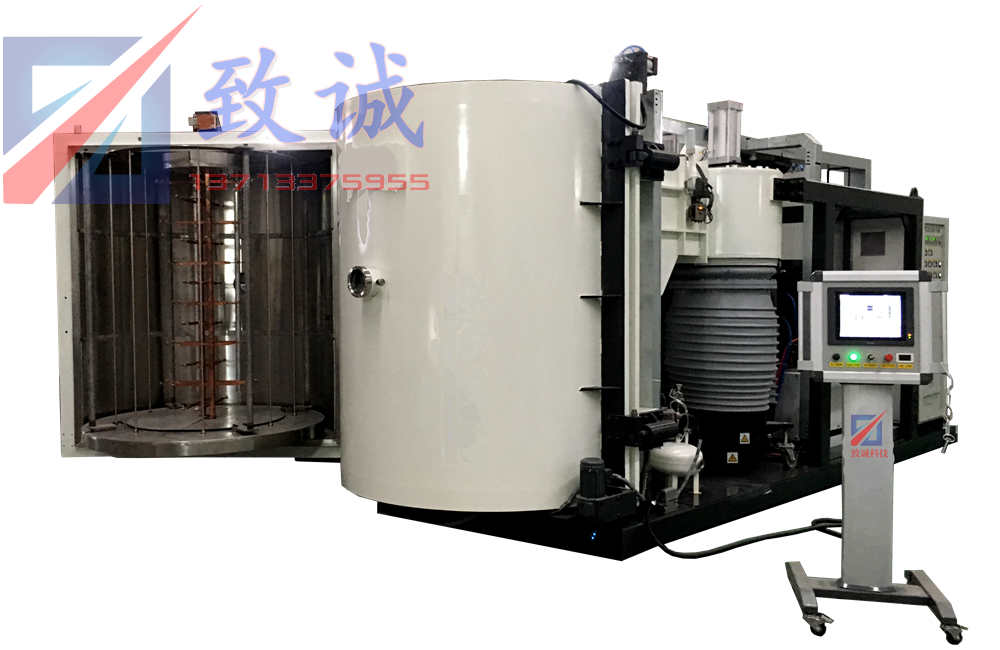
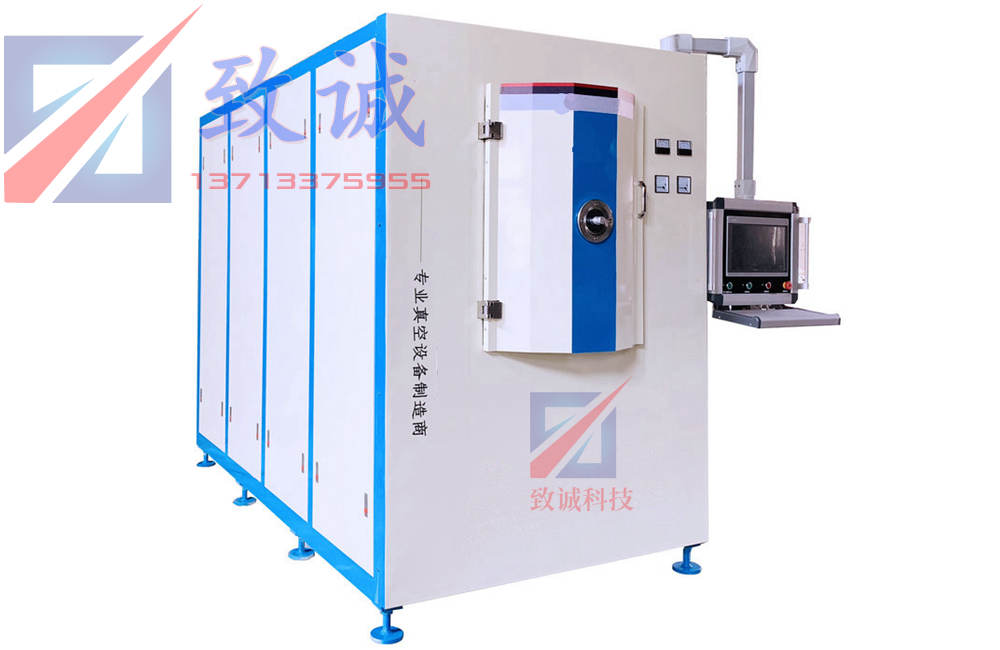
PRODUCTS
















